The advantages of telemedicine technology exceed expectations: telemedicine has proven to be beneficial for providers and patients. Telemedicine can sometimes achieve better outcomes than in-person visits. Its use increases patient retention by 81.5% and dramatically reduces costs. In Philadelphia, adopting a telemedicine platform saved one hospital up to $1,500 per hospital visit and up to $120 per patient visit.
Keep reading to learn the main trends in telemedicine software development, typical app functionality, and stages of the development process with estimated costs per stage.
Telehealth software development trends after COVID

Telemedicine is not a novelty: clinics have been using it for decades. Yet, its adoption was a slow process until COVID-19, but the pandemic has caused the use of telehealth to skyrocket from 11% to 76% within a year. Patients canceling in-person care and the government shutting down medical facilities forced both regulatory organizations and providers to adapt aggressively to a new situation.
COVID-19 has resulted in 80 new approved telehealth services, and many earlier restrictions have been lifted. New laws are now forcing insurers to cover virtual health services in the same way they cover in-person visits. Loosened restrictions have allowed providers to rapidly increase their telehealth offerings up to 50-146 times on average.
Looking ahead at trends in telecare, what do we expect from telemedicine technology and clinical applications in the near future? Here’s a short list.
First primary care apps
Research shows that 97% of primary care practitioners used telemedicine in 2020. Practitioners will likely continue using telemedicine platforms for follow-ups and nonurgent care. This will result in better functionality of healthcare consultation apps.
Specialty care-enablement apps
Not all specialties will benefit equally from telemedicine. It may be harder to implement for practices based on specialty procedures such as ophthalmology or surgery. However, we can incorporate virtual tools into specialty care delivery. For instance, there’s been an increase in use for telepsychiatry and a growing number of pre- and postsurgical virtual consultations.
Telemedicine software development will become more complex. As a result, the number of specialty care-enablement telemedicine platforms will continue to grow. This growth can reinvent specialty care in weeks, as we saw happen with cardiovascular care. After adopting a specialized telehealth platform, virtual visits of cardiovascular patients went from zero to 75% within just 14 days.
More advanced apps for video visits
The growing use of video visits by medical staff, patients, their family and friends will likely result in more advanced video apps designed specifically for a care setting rather than personal or business communication.
Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM)
For better treatment outcomes, practitioners collect patient health data using RPM technologies along with video consultations. RPM tools have proven to be more effective and reliable for examining risk factors than traditional methods. RPM allows practitioners to discover potentially harmful factors affecting patient health and detect disease or complications at an earlier stage. With that said, RPM tools are likely to evolve into more complex systems addressing a wider range of health parameters.

Technology trends in telehealth software development
Expanded use of AI-tools. Telemedicine platforms and RPM tools widely use artificial intelligence. They are used in advanced chatbots, for speech recognition, voice search, machine learning, etc. AI-based chatbots consult patients about their symptoms, generate health data, and hand off the conversation to health experts if needed. While providing safer and faster care to patients, AI-based solutions allow providers to enhance triage efficiency and decrease call center volume and related costs. Research confirms that clinical health AI apps can potentially save $150 billion each year.
Blockchain. The use of blockchain technology allows telemedicine app developers to decentralize highly encrypted data. In other words, encrypted health records are divided and stored across a network of computers. This results in a higher data security level and a growing number of healthcare apps leveraging blockchain.
Internet of Things (IoT). Connecting telemedicine equipment like tablets, smartwatches, phones, etc., contributes to better tracking of health parameters, diagnosis, medical adherence, and more.
Augmented Reality (AR). Telehealth platforms can use AR for healthcare data visualization or digital interface during video consultations. AR improves the patients' experience and increases engagement.
We've mentioned the main tech trends in healthcare to consider, but there are more we could list. Now, let’s talk about the functionality of telehealth apps and how it differs for doctor and patient apps.
Telemedicine software features to consider
Features of telemedicine solution may vary depending on the software’s purpose and whether it’s used by patients or practitioners. When considering building vs. buying a telemedicine platform, keep in mind that with tailored functionality, custom solutions will cost you less in the long run.
Two important telemedicine software features to consider are:
-
Data security. Telehealth security should include data encryption and HIPAA compliance. You may also consider developing blockchain-based software.
-
Multi-platforms approach. The app should run smoothly on iOS and Android mobile platforms, as well as on the web.
Patient software
If your software is used by patients, consider implementing the following features:
-
Communication. The main feature of patient telehealth software is online real-time consultations. These can be conducted via chat, audio, or video calls. Specialty-enablement software for dermatologists, for example, can use photo-based consultations.
-
Registration and patient profile. Make sure that users can sign up via email, social network, or with a phone number. Consider making the patient profile simple, with auto-filling fields, so users don’t have to fill out lengthy forms.
-
Advanced search. Users need the ability to search for specialists based on several criteria such as specialization, availability, rating, and price.
-
Scheduling. Software should show users a list of their appointments (even better if shown as a calendar). It should also let them pick the date and time based on doctor availability and edit (or cancel) appointments if necessary.
-
Notifications. By using push notifications and reminders, apps can alert users about upcoming appointments.
-
Geolocation. To show available doctors with a valid license in a particular area, software needs to gather user location.
-
Mobile payment. Gateway systems like PayPal or Braintree usually integrate smoothly with telemedicine software.
-
Rating system. With this feature, you can collect user feedback about the app's functionality and performance. For a doctor-patient aggregator, users' ratings are necessary to assess the quality of the services provided.

Depending on the purpose of the software, it can include more specific functions, such as:
-
Navigation for adding routes. Some apps can also allow users to book a taxi.
-
Medication tracking to remind users about taking their medications. This function often allows users to renew their prescriptions automatically. They can even order delivery of their medicines from drug stores through some apps.
-
Medication advice for patients who have questions about their prescriptions and feel uncomfortable asking their doctor.
-
Integration with the insurance provider will add the patient's insurance plan.
-
Advanced patient profiles with dashboards will show patients their treatment progress.
Practitioner software
Though many features can correlate, software for doctors has several specific features addressing the doctor’s needs. But first, let’s take a look at the overlapping functionality.
-
Communication and recording. Doctors should be able to save consultations to check on treatment progress.
-
Registration and doctor’s profile. Doctors should be able to attach their licenses and certificates. You may also consider adding an auto-filling option. For example, the software will scan documents uploaded by doctors and extract necessary information about their education or experience.
-
Scheduling. Doctors should be able to receive consultation requests, set their availability, and manage the calendar.
Specific features for practitioners’ telemedicine software will include:
-
EHR review. Doctors should be able to check patient records, profiles, data from medical institutions, or other data sources.
-
Medical prescription. Software should enable practitioners to place the prescription digitally, which is particularly efficient for patients with ongoing prescriptions.
-
Analytics. Doctors need to check the treatment progress and prescription history. Dashboards with analytics will help them make adjustments to the treatment process if necessary.
-
Integration with pharmacy databases. Integration with drug stores will prevent doctors from prescribing rare, unavailable, or outdated medications.
This is not an exhaustive list of telemedicine app features, but it’s a good start to help decide which functions you may want to include in your software. Now, let’s turn to some examples of successful telemedicine apps on the market.
3 telemedicine software platforms to check out before developing yours
Knowing your competitors and their pros and cons comes in handy if you plan to develop a telemedicine platform. Here are the three most popular ones.
Teladoc
Teladoc is a patient-oriented, HIPAA compliant telemedicine platform, allowing patients to access a network of doctors. The platform is available in 16 countries, including European countries, the US, South America, Australia, and China.
The service provides strictly non-emergency care, with emergency calls being routed through to a proper hospital. Practitioners can prescribe only regular medications without controlled substances. Because the platform handles only routine medical advice and care, relationships between doctors and patients are short.
Users can access the platform through mobile apps or desktops.
|
Pros |
Cons |
|
|
Doxy Me
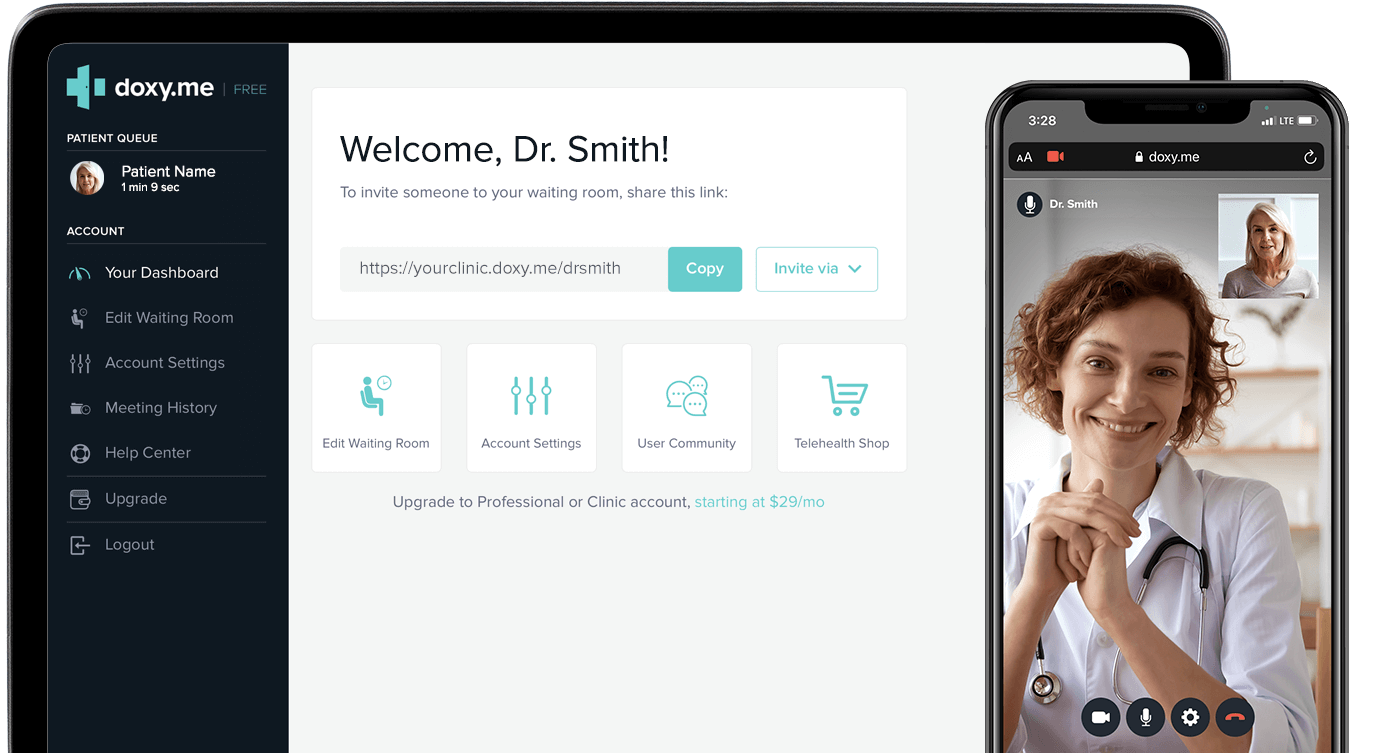
Doxy Me is a simple, HIPAA-compliant telemedicine platform designed for healthcare practitioners. More than 700,000 providers use the platform in 136 countries. It enables them to communicate with patients through live chats or video calls, create personalized waiting rooms, track queues, and view meeting history. The platform is free, although it offers additional features like audio communication, group calls, screen share, or file transfer for paid tiers.
The platform can run in any browser. It easily integrates with EHR or PM software and does not require setting up. It also offers custom telehealth app solutions for large enterprises.
|
Pros |
Cons |
|
|
AmWell
American Well (AmWell) is a feature-rich telehealth platform used by 80 million patients and 70,000 care providers. Their partnership with insurance giants allows them to stand out from competitors.
The platform handles acute and chronic care, pediatric, population health management, telepsychiatry, and other fields.
Amwell easily integrates into a company workflow. It also supports integration by offering clinical coverage and training and implementation services.
|
Pros |
Cons |
|
|
Now that you’ve considered the features your application is going to offer and how it will differ from competitors, it’s time to look at the development process in more detail.
Stages of telemedicine software development
The telemedicine app development process can be divided into discovery and development stages.
Discovery stage
Idea evaluation. Telehealth software development starts with the business, market, and competitor analysis to define your concept, value proposition and decide on the functions.
Know the laws. Telemedicine information exchange should comply with existing regulations related to EHR security: GDPR, HIPAA, HITECH, etc. Though standards may vary depending on the area, software purpose, and functions, in most cases, you will need to focus on the following factors:
-
Company or person authentication
-
Access control
-
Data integrity and transmission security
-
Audit trails and activity logs
Prototyping and design. Consider developing a low-fidelity prototype first. At this stage, you will need UX/UI designers to create an app interface and layout based on your purposes and desired functions. Keep in mind that the design should be simple, intuitive, and logical to ensure that navigation is smooth and effortless for users.

Development stage
Planning. After project confirmation, the development team arranges the process and plans deadlines for each stage.
Development. At this stage, engineers are writing the code. You may consider developing a basic version of the app first or an MVP. A fast market release will help to collect feedback and improve the app before further scaling. This will also help your budget because the release of a fully-featured app costs significantly more.
Scalability and high performance. Try finding a reliable development team that can build a telemedicine system and handle its scaling and maintenance. Even a perfectly developed platform will crash due to a growing workload if it has scalability problems.
Quality assurance and testing. After finishing coding, it’s time to test the app’s performance and functioning.
Tech stack
We have mentioned some of the technology trends in healthcare, like blockchain, IoT, AR, and AI. Apart from these, here are some more commonly used technologies in telemedicine platforms:
-
Cloud-based data storage. Healthcare is one of the industries where demand for cloud services is skyrocketing. Providers searching for HIPAA-compliant telemed apps and storage solutions are turning to the cloud as a low-cost option for developing complex infrastructures.
-
API integration. You don’t need to develop many typical functions like encrypted video calling, instant messaging, or a live chat from scratch. It’s expensive and requires both time and effort. Instead, focus on API integration and use out-of-the-box third-party solutions.
-
EHR system integration. EHRs are patient health records in a digital format with instant and secure access, and your telemedicine app should integrate with EHRs perfectly.
-
Health trackers integration. When developing apps with health monitoring functions, consider integration with Google Fit (for Android operating systems) or Apple HealthKit (for iOS).
Telemedicine website development
Mobile apps are comfortable to use for patients, but they can be difficult for hospitals and practitioners who commonly use web-based platforms.
Another drawback is the cost. Obviously, developing an app that can work on both mobile platforms and on the web can cost you a fortune. If you’re not ready for such an investment, the best choice is telehealth website development. It will be mobile-flexible and equally compatible with tablets and laptops.
Telemedicine software costs: developing and maintaining
The cost of a telemedicine app will vary depending on the country, project concept, functionality, approach, and vendor.
Research
On average, discovery and initial research (business, market, and competitors analysis) will likely cost you up to $10,000. You can save this money if your company does the research without hiring third-party specialists.
The UX/UI designer will need one or two months to design the user interface and experience. This will cost around $10,000-$15,000 in total.
Development process
These expenses will vary greatly depending on the platforms that need to be covered, the number of team members, the infrastructure, whether you’ll hire developers in-house or consider outsourcing, and more.
Maintenance
Ongoing app development is often undervalued. Yet, in the long run, it is considerably higher than one-time development. It will run you 15-20% of the initial cost each year. This includes app infrastructure maintenance (hosting, servers, clouds, or domains), telemedicine equipment cost, API integrations, and other services, regular app updates and fixing bugs, etc.
How can Demigos help to build a telemedicine platform?
Demigos has built the MSHFA app, a multilingual, HIPAA-compliant telemedicine and EMR platform for a Kuwaiti clinic. The platform comprises a mobile app for patients, a web app for doctors, another web app for pharmacists, and an admin panel. It supports video conferencing between doctors and patients, stores medical records, and allows patients to order medication via the app.
See the case study: https://demigos.com/case-mshfa/
 Demigos is a top-rated development vendor specializing in health tech. We handle every stage of development: from research and design to coding and support.
Demigos is a top-rated development vendor specializing in health tech. We handle every stage of development: from research and design to coding and support.
At Demigos, instead of “silent coding,” we generate ideas on how to improve product performance, design, and positioning based on our experience building complex health tech solutions.
For instance, our other telemedicine platform, along with proper SEO optimization, helped our client increase the number of users by 50 times without any marketing efforts.
Our solutions are flexible, highly scalable, and comply with HIPAA and GDPR standards. To ensure secure telemedicine app development, we follow best practices for detecting vulnerabilities, assessing architectural risks, and performance under cyber attacks.
Have a project in mind?
Healthcare has always been on the cutting edge of innovation. COVID-19 has accelerated improvements in the area of telemedicine by giving us the opportunity to shift toward virtual care delivery. New telehealth technologies are evolving at breakneck speed, and more companies are choosing to use telemedicine software development and implementation to stay current with the times.
Now is the best time for building custom telemedicine software. The upward trend for virtual healthcare will continue with more advanced solutions entering the market. Telemedicine tools are what will help you to ride the industry's tailwind and stay ahead of competitors.
If you’re thinking about how to develop a telemedicine app, Demigos is here to free you from administrative and development headaches. Just contact us and tell us more about your ideas.






